In the world of industrial shredding, processing difficult-to-shred materials requires specialized machines designed to handle challenging textures, densities, and structures. Whether it's shredding complex car seats, fiber-reinforced plastics (FRPs) or other difficult-to-shred materials, the right equipment is crucial for efficiency and productivity. This article explores the complexity of shredding difficult-to-shred materials, the specific challenges, and the available machine solutions to address them. Purchasers of industrial equipment, engineers, and technical staff will find this guide invaluable for selecting and optimizing shredder solutions for challenging materials.
Understanding the Challenges of Shredding Difficult-to-Process Materials
Difficult-to-shred materials vary significantly, but some common characteristics make them challenging to shred, such as:
- Density – Heavier, denser materials like metal-reinforced plastics can cause wear and tear on standard shredder equipment.
- Hardness – Materials such as auto parts and reinforced plastics can be incredibly hard, requiring robust machines with specialized cutting mechanisms.
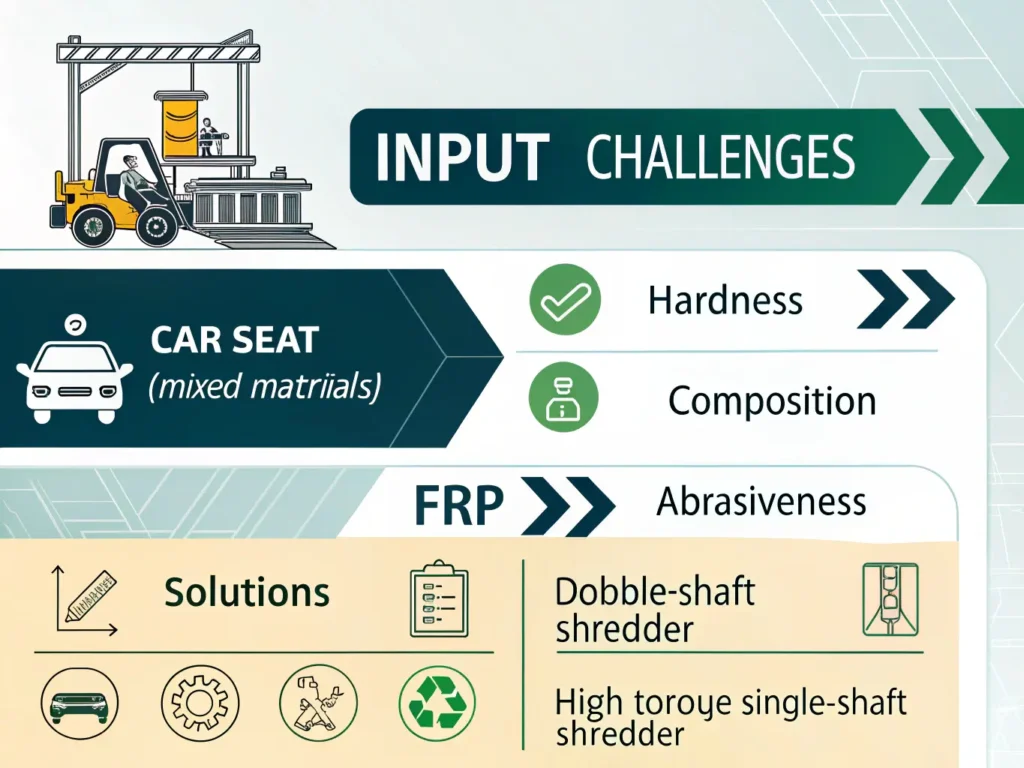
- Complex Composition – Many difficult-to-shred materials, such as car seats or fiber-reinforced composites, consist of a variety of materials, including metal, foam, and fabric, which must be separated during the shredding process.
When these characteristics are present, industrial shredders must be built with durability, precision, and flexibility in mind. Let's delve deeper into two of the most common difficult-to-shred materials: car seats and fiber-reinforced plastics.
Car Seat Shredders: A Complex Task
Composition of Car Seats
Car seats are generally made up of a mixture of materials, including:
- Foam: The soft, cushion-like material that provides comfort.
- Dust: Textiles made from polyester or other synthetic fibers.
- Metal Components: The frame and mechanical parts often contain steel or aluminum.
- Plastic Parts: Components such as the headrest or armrests are made from various types of plastics.
This blend of materials presents unique challenges, especially when metals are not removed before shredding, which can lead to potential damage to the equipment and difficulties in separating the materials after processing.
** The Solution:
**
- Double-shaft shredders **.
- A double-shaft shredder is an ideal solution for shredding car seats due to its ability to process mixed materials. The robust design of the machine features two rotating shafts that turn in opposite directions, efficiently shredding even tough materials. The process for shredding car seats generally involves: **.
- Initial pre-shredding: **.
With these machines, manufacturers can improve processing efficiency and reduce the time required to separate materials after shredding.
Fiber-Reinforced Plastics (FRP): Stiffer and More Complex
What are Fiber-Reinforced Plastics?
Fiber-reinforced plastics (FRPs) are composite materials that contain fibers such as glass, carbon, or aramide within a plastic matrix. Known for their incredible strength-to-weight ratio, they are highly effective in industries such as the automotive industry, aerospace, and construction. However, their unique composition also makes them difficult to shred with standard equipment.
The Challenge: Sustainability and Abrasiveness
FRPs present several challenges for shredder machines:
- Abrasiveness: The fibers used in FRPs can cause significant wear on shredder blades, requiring specialized materials and coatings to extend the lifespan of the equipment.
- Toughness: The high tensile strength of FRPs makes them difficult to shred, requiring high torque and specialized cutting mechanisms.
The Solution: High-Torque, Heavy-Duty Shredders
Shredding VVK's requires heavy-duty machines capable of handling high torque and dealing with abrasive materials. A single-shaft shredder with high torque is often the best choice for this type of material. These machines are designed to shred tough materials by using robust blades and powerful motors to generate enough force to break through the fibers.
The shredding process generally involves:
- Input: The VVK material is fed into the shredder via a conveyor belt or an automated system.
- Shredding: The high-torque motor of the shredder rotates blades to tear apart the composite material.
- Separation: After shredding, the resulting pieces are sorted, often using air classifiers or screens, to separate the fibers from the plastic matrix.
Optimize for Longevity
To extend the lifespan of equipment used in the shredding of VVKs, wear-resistant cutting blades and wear-resistant linings are employed. These features help ensure that the shredder can handle the demanding nature of VVKs without significant damage.
Important Considerations When Choosing Shredder Equipment
When selecting a shredder for challenging materials such as car seats or fiber-reinforced plastics, several factors must be taken into account:
- Material Composition
Understanding the exact mix of materials being shredded is crucial. For example, car seats with embedded metals require a shredder with magnetic separation, while VVKs demand high torque and wear-resistant components. - Shredder Design
For difficult-to-process materials, a dual-shaft shredder or a single-shaft shredder with high torque is generally most suitable. These machines are capable of easily processing tough, dense materials, and their robust designs minimize downtime and maintenance. - Processing Speed
Shredding challenging materials can be time-consuming. Choosing a shredder with adjustable speeds and the ability to handle high throughput can ensure efficiency and minimize bottlenecks in the production process. - Maintenance and Wear Resistance
Difficult materials can accelerate wear on shredder knives. Choosing machines with replaceable knives, wear-resistant coatings, and high durability components helps to lower total ownership costs and extend the lifespan of the equipment.
Conclusion
Shredding difficult-to-process materials such as car seats and fiber-reinforced plastics requires specialized machines designed to handle the complexity of mixed compositions and tough fibers. Double-shaft shredders are ideal for mixed materials like car seats, while heavy-duty shredders with high torque are essential for fiber-reinforced plastics. By selecting the right equipment and ensuring proper maintenance, manufacturers can improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and optimize recycling processes.
Make sure your shredder can handle the task! Choosing the right machine for the job is essential for maximizing productivity and ensuring long-term reliability when processing challenging materials.
For more information on shredder equipment for difficult materials, contact our expert team. We offer customized solutions to meet the needs of industries dealing with complex recycling and shredding processes.
Ready to upgrade your shredder equipment? Let us help you select the right machine to easily process your most challenging materials.


 PVC Window & Door Profile Granulator | uPVC Profile Breaker for Recycling
PVC Window & Door Profile Granulator | uPVC Profile Breaker for Recycling Granulators for Hard Plastics
Granulators for Hard Plastics