The choice between a plastic granulator versus a grinder (or pulverizer) is a critical decision in plastic processing that has direct implications for efficiency, energy costs, and the quality of your final product. Although both machines reduce material size, their operating principles, output, and applications are fundamentally different. A wrong choice can lead to unnecessary energy consumption, suboptimal material quality, and production downtime. This guide is specifically designed for engineers, production managers, and buyers in the recycling and plastic industries. We analyze the technical differences so that you can make a well-considered decision that perfectly fits your process requirements. At [Company Name], we help our customers daily with selecting the right equipment. A granulator is a machine designed to cut larger pieces of plastic, such as waste products, bottles, profiles, or films, into small, uniform particles. These particles are called "regrind" or "flakes" and are directly suitable for reuse in production processes.
Key Principles of a Granulator: Rumtoo Machine Mechanism:
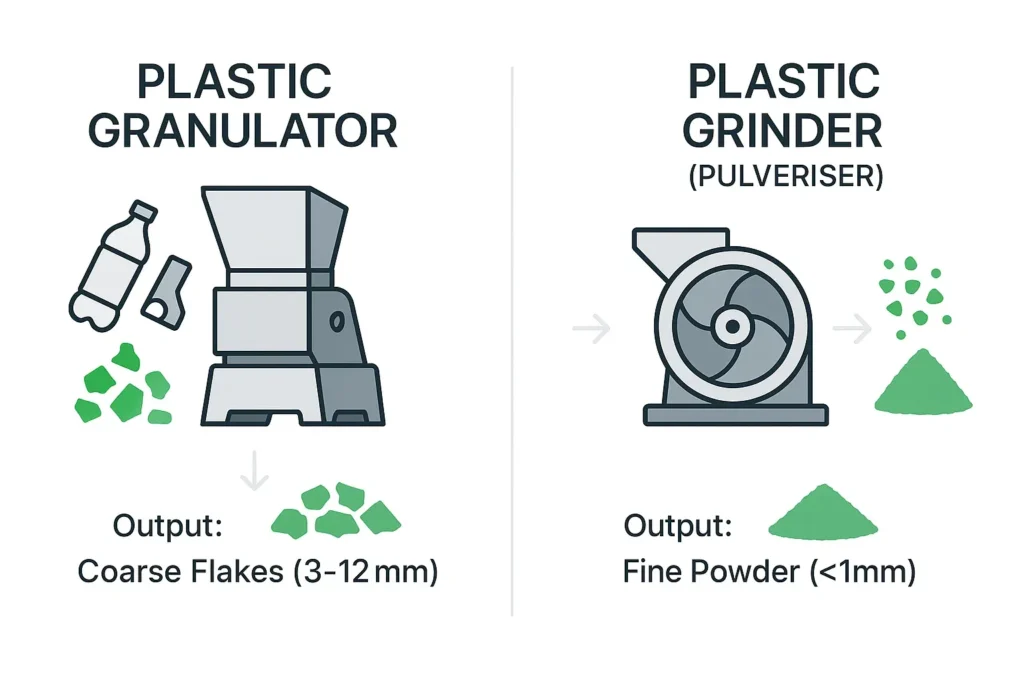
What is a Plastic Granulator?
A Plastic granulator A granulator works like a robust scissor. Rotating blades on a rotor cut the material against fixed, stationary blades in a cutting chamber. Output Control: A perforated sieve under the cutting chamber determines the maximum size of the final product. The material circulates in the chamber until it is small enough to fall through the sieve holes.
Final Product:
- The output is a relatively uniform granulate (flakes), usually between 3 mm and 12 mm in size, with an irregular, angular shape. Typical Applications:
- Granulators are the workhorses for volume reduction and creating reusable material. They are primarily used for: Direct processing of production waste (e.g., sprues, rejected parts) for reuse in injection molding or extrusion processes.
- Pre-reduction of material in a large-scale recycling line before it goes to a washing facility. Volume reduction of long and bulky waste to lower transportation and storage costs.
Standard Plastic Granulators
For efficiently reducing plastic waste to high-quality regrind. Our granulators are built for durability and easy maintenance, ideal for direct integration into your production line.
- View Models & Specifications
- What is a Plastic Pulverizer (Grinder)?
- Although the term 'grinder' is sometimes used, the technically correct name is
pulverizing
of plastic (often pre-granulated) into a very fine powder. Key Principles of a Pulverizer: %% Instead of cutting, a pulverizer works through impact and friction. A commonly used type is the disc mill, where the material is crushed between one or two very fast rotating, toothed discs.The fineness of the powder is precisely controlled by the distance between the discs, the disc design, and often an air classification system that separates the final product. The output is a fine, free-flowing powder, generally smaller than 1 mm (1000 micron), often specified in 'mesh' or micron (e.g., 300-800 micron). Pulverizers are specialized machines needed when the final product must be a powder. The main applications are:
Production of plastic powder for
- The output is a relatively uniform granulate (flakes), usually between 3 mm and 12 mm in size, with an irregular, angular shape. rotomolding
- Granulators are the workhorses for volume reduction and creating reusable material. They are primarily used for: (rotomolding), a process where powder is melted in a mold.
- Pre-reduction of material in a large-scale recycling line before it goes to a washing facility. Creating fine additives or fillers for compounding processes.
Standard Plastic Granulators
Production of masterbatches and PVC compounds for pipes and profiles.
- PVC Pulverizer / Micronizer Transform plastic granulate into fine, uniform powder with our advanced pulverizers. Perfect for rotomolding, compounding, and other applications that require precise particle size. Discover Our Systems
- Granulator vs. Grinder: The Direct Comparison
- The following table highlights the main technical and operational differences.
Final Product
Chips/flakes (approx. 3mm – 12mm)
| | Primary Goal | Product safety for market access | Workplace safety during use and maintenance | | Plastic Granulator | Powder (generally < 1mm / 1000 micron) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Operating Principle | Cutting / shearing (knives) |
| Impact / friction / crushing (discs/hammers) | Typical Feed Material | Large plastic parts, waste, film |
| Pre-granulated material (flakes) | High (requires a lot of energy to make powder) | Application Output |
| Direct reuse (injection molding, extrusion) | Specialized processes (rotomolding, compounding) | Decision Guide for Professionals |
| Energy Consumption | Average | Use this checklist to quickly identify the right machine: |
| When should you choose a GRANULATOR? | Direct hergebruik (spuitgieten, extrusie) | Gespecialiseerde processen (rotatiegieten, compounding) |
Beslissingsgids voor Professionals
Gebruik deze checklist om snel de juiste machine te identificeren:
Wanneer kiest u voor een GRANULATOR?
- Your goal is: To reduce waste volume and make it directly reusable in your existing machines (injection molding, extrusion).
- Your input is: Large, bulky parts, sprues, bottles, or thick film.
- Your output must be: Uniform particles of a few millimeters in size (regrind).
When is a PULVERIZER (GRINDER) the right choice?
- Your goal is: To produce a fine powder as the final product for a specific process.
- Your input is: Generally, already reduced material (granulate).
- Your output must be: A powder with a precisely defined, very fine particle size (measured in microns or mesh).
The Two-Step Solution: Granulator + Pulverizer
In many cases, these machines work together. A granulator performs the first, coarse reduction. The resulting granulate is then fed into a pulverizer for the fine grinding to powder. This is the most energy-efficient method to convert large waste into fine powder.
Conclusion: The Right Machine for the Right Task
The difference between a plastic granulator and a grinder (pulverizer) is clear: the granulator slices material into reusable flakes, while the pulverizer grinds it into fine powder for specialized applications. The choice depends entirely on your desired final product and downstream process.
By selecting the right technology, you not only optimize your material flow but also reduce your operational costs and increase the value of your recycled materials. A granulator is the start of many recycling cycles; a pulverizer is the key to high-quality powder applications.